Приложение принимает две буквы в качестве аргументов командной строки. Если переданы правильные буквы - оно выведет флаг.
Solution
Глянув строки с помощью strings, я ничего интересного не нашел. С недавних пор я пробую использовать локальные LLM в процессе реверса. Планирую об этом написать большую статью, а пока буду пробовать разные штуки)
main
Попросил LLM переименовать за меня переменные. А пока сам разберу main:
int32_t main(int32_t argc, char** argv, char** envp)
{
void* const __return_addr_1 = __return_addr;
int32_t* var_c = &argc;
void* gsbase;
int32_t ecx = *(uint32_t*)((char*)gsbase + 0x14);
int32_t result;
if (argc > 2)
{
int32_t str;
__builtin_strcpy(&str, "dix_gyhiiz}xdduah}puvyhn}u}pxa}tnbfh}ozbc");
int32_t eax_6 = (int32_t)get_idx(*(uint8_t*)argv[1]);
int32_t eax_13 = (int32_t)get_idx(*(uint8_t*)argv[2]);
if (eax_6 == 0xffffffff || eax_13 == 0xffffffff)
{
puts("Sorry, bro");
result = 3;
}
else
{
decode(&str, (uint8_t)eax_6, (uint8_t)eax_13);
puts(&str);
result = 0;
}
}
else
{
puts("WHAAAAAT?");
result = 2;
}
if (ecx == *(uint32_t*)((char*)gsbase + 0x14))
return result;
__stack_chk_fail();
/* no return */
}
Как и было сказано в условии, на вход нужно передать 2 символа. Они передаются в функцию get_idx. Судя по названию, мы получаем индекс символов. Но я это гляну еще чуть позже. По сути нас интересует вот эта часть кода:
if (argc > 2)
{
int32_t flag;
__builtin_strcpy(&flag, "dix_gyhiiz}xdduah}puvyhn}u}pxa}tnbfh}ozbc");
int32_t c_1 = (int32_t)get_idx(*(uint8_t*)argv[1]);
int32_t c_2 = (int32_t)get_idx(*(uint8_t*)argv[2]);
if (c_1 == -1 || c_2 == -1)
{
puts("Sorry, bro");
result = 3;
}
else
{
decode(&flag, (uint8_t)c_1, (uint8_t)c_2);
puts(&flag);
result = 0;
}
}
else
{
puts("WHAAAAAT?");
result = 2;
}
Функция get_idx
Код не сложный. Но ради любопытства попрошу LLM объяснить его мне)
uint32_t get_idx(char arg1)
{
int32_t var_8 = 0;
char var_9 = 0xff;
for (int32_t i = 0; i <= 28; i += 1)
{
if (alph[i] == arg1)
var_9 = (uint8_t)i;
}
return (uint32_t)var_9;
}
Не удобно читать в логах, нужно будет подумать над этим. Вот ее вывод:
[Default] Function Explanation:
[Default] The main purpose of this function is to perform a case-insensitive search for the first occurrence of a specific character in a given string. It takes two input parameters: `arg1` which is the character to be searched, and a string represented by the pointer `*"abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz{}_"`. The function returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified character in the string.
[Default]
[Default] Input parameters:
[Default]
[Default] * `arg1`: the character to be searched.
[Default] * `*"abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz{}_"`: a string represented by a pointer.
[Default]
[Default] Return value:
[Default] The function returns an integer representing the index of the first occurrence of the specified character in the string, or -1 if the character is not found.
[Default]
[Default] Key operations and algorithms used:
[Default] The function uses a simple linear search algorithm to find the first occurrence of the specified character in the given string. It iterates over each character in the string and checks if it matches the specified character using the `==` operator. If a match is found, the index of the character is returned immediately. If the end of the string is reached without finding a match, -1 is returned.
[Default]
[Default] Important code patterns or structures:
[Default] The function uses a loop to iterate over each character in the string and check if it matches the specified character. The loop continues until either a match is found or the end of the string is reached.
[Default]
[Default] Notable edge cases or error handling:
[Default] The function does not handle any edge cases or errors. If the input string pointer is null or points to an invalid memory location, the behavior of the function is undefined. Additionally, if the specified character is not found in the given string, the function will return -1 without any indication of whether this is due to the character not being present in the string or some other issue.
[Default] ------------------
Для тех, кто не знаком с гуглом:
Основная цель этой функции — выполнить поиск первого вхождения заданного символа в строке без учёта регистра. Она принимает два аргумента:
arg1— символ, который нужно найти;- строку, представленную указателем
*"abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz{}_”. Функция возвращает индекс первого появления указанного символа в этой строке.
Тут он немного погорячился, ведь у нас только один аргумент. Но по сути верно. Эх, ИИ заменит людей, говорили они…
По сути функция ищет первое вхождение символа в строке abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz{}_. Возвращает его позицию или -1, если не найдет.
Символы нам не известны, значит нужно брутить 28 * 28 комбинаций.
Функция decode
Разберем функцию декодирования:
int32_t decode(char* flag, uint8_t c1, uint8_t c2)
{
size_t len = strlen(flag);
char* flag_1 = flag;
int32_t i;
for (i = 0; i < len; i += 1)
{
*(uint8_t*)flag_1 = transform(*(uint8_t*)flag_1, c1, c2);
flag_1 = &flag_1[1];
}
return i;
}
Так-с. Тут каждый символ флага заменятся результатом выполнения transform от символа флага и ключей, которые мы передаем.
Функция transform
Вот он - последний шаг. Ну или не последний…
uint32_t transform(char arg1, char arg2, char arg3)
{
char eax_2 = get_idx(arg1);
if (eax_2 != 0xff)
return (uint32_t)alph[((int32_t)eax_2 * (int32_t)arg2 + (int32_t)arg3) % 0x1d];
puts("Wrong input");
exit(0);
/* no return */
}
Модульная арифметика:
alph[(ind * c1 + c2) % 29];
Думаю, что тут вполне всё понятно.
Пишем solver
Если обобщить, то нам нужно перебрать 28 * 28 пар символов, чтобы найти заветный ключ. Погнали. Я уже говорил про LLM, так вот. Закину промт)
# brute_transform.py
# Python 3.x
# Brute-forces all pairs (c1, c2) for the given decoder algorithm
# based on the provided C code.
alph = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz{}_"
def get_idx(ch: str) -> int:
"""Return index of character in alph or -1 if not found."""
try:
return alph.index(ch)
except ValueError:
return -1
def transform(arg1: str, c1: str, c2: str) -> str:
"""Python version of the C transform() function."""
ind = get_idx(arg1)
if ind == -1:
return None
result_index = (ind * get_idx(c1) + get_idx(c2)) % 29
return alph[result_index]
def decode_flag(encoded: str, c1: str, c2: str) -> str:
"""Apply transform() on each character of encoded string."""
decoded = []
for ch in encoded:
dec = transform(ch, c1, c2)
if dec is None:
return None
decoded.append(dec)
return "".join(decoded)
def main():
encoded_flag = "dix_gyhiiz}xdduah}puvyhn}u}pxa}tnbfh}ozbc"
# brute-force all pairs of c1, c2 from alph
for c1 in alph:
for c2 in alph:
decoded = decode_flag(encoded_flag, c1, c2)
if decoded is None:
continue
# optional heuristic: only print if result looks readable
if all(32 <= ord(ch) < 127 for ch in decoded):
print(f"[{c1}{c2}] -> {decoded}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Никакого удаления французского. Годится. Запускаю:
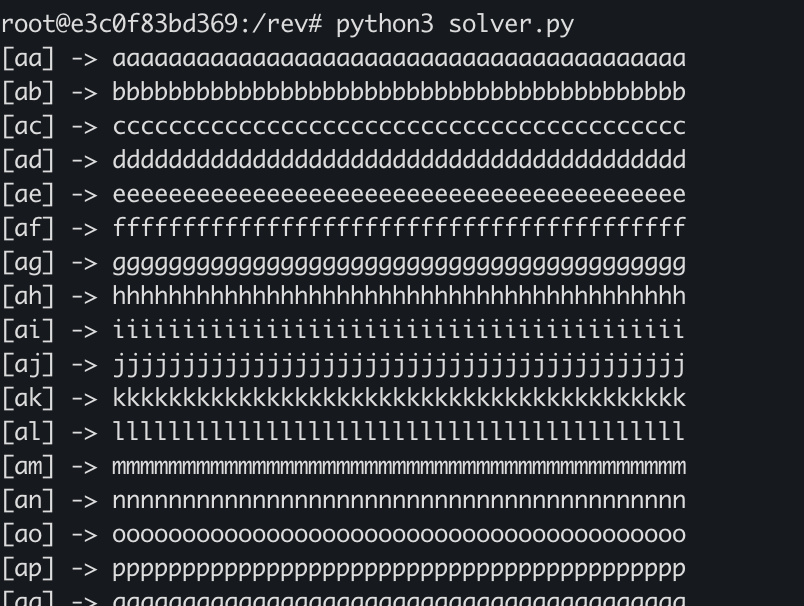
Красотища. Попробую использовать grep flag, чтобы найти ответ:
root@e3c0f83bd369:/rev# python3 solver.py | grep flag
[hn] -> flag{hello_affine_cipher_i_can_brute_you}
Проверю на оригинальном бинаре. Мало ли…
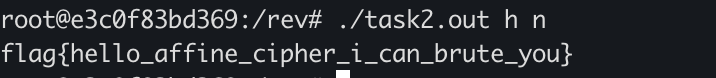
Подошло. Так-с. А что за affine_cipher?!
Аффинный шифр
Подстановочный шифр. В аффинном шифре каждой букве алфавита размера m ставится в соответствие число из диапазона 0…_m_-1. Затем при помощи специальной формулы вычисляется новое число, которое заменит старое в шифртексте.
А процесс шифрования можно описать следующим образом:
E(x) = (ax + b) mod m
Где:
x— номер шифруемой буквы в алфавите;m— размер алфавита;a,b— ключ шифрования.
